PERIODONTICS
Periodontics: treatment of the tissues (bone and gums) supporting the teeth
Periodontics is the branch of dentistry that deals with all the tissues around the tooth, including the gums and alveolar bone. Periodontal diseases are usually chronic and asymptomatic.
However, patients with periodontitis often observe gum withdrawal above the teeth, commonly known as “gum disease”. At Smile and Care, our periodontology specialist holds Swiss federal certification, and treats all periodontal diseases. To do this, a clinical and radiological assessment is required to establish the diagnosis, along with a treatment plan and quote.

LEARN MORE ABOUT PERIODONTAL DISEASES:
1. Gingivitis, the first stage of periodontitis
How do I recognize it?
Healthy gums are pink, firm, and do not bleed. If the teeth are not brushed regularly and properly, the bacterial plaque on the surface of the teeth forms tartar. The more tartar there is on the teeth, the more the gums are attacked.
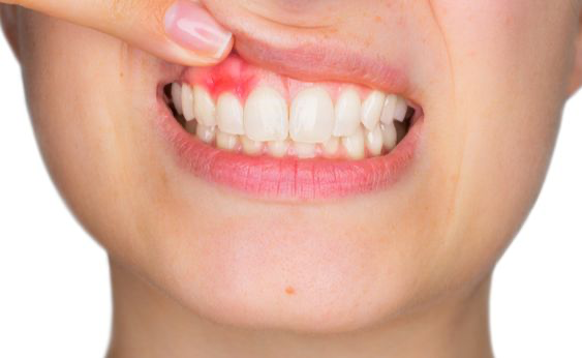
This tartar causes inflammation of the gums. They become irritated, swollen and start bleeding – a condition known as “gingivitis”. Gums can easily bleed, especially when brushing teeth. While this disease is common and can be asymptomatic, it is important to treat it as quickly as possible to prevent it from developing into a more serious disease, such as periodontitis. Without treatment, gingivitis can spread to the gums, bones, and tissues around the teeth.
How is gingivitis treated and prevented?
Thanks to dental scaling and brushing habits that are reviewed according to the patient and his or her risks, gingivitis can be easily reversible. These new oral hygiene habits will serve as the basis for maintaining healthy gums.
In short, the best way to fight this disease is to adopt good, daily oral hygiene to remove plaque before it turns into tartar.
2. Periodontitis
How do I recognize it?
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease caused by bacteria that affects the tissues supporting teeth, including the gums and bone. There are two forms of periodontitis: aggressive periodontitis – which evolves rapidly – and chronic periodontitis, which occurs more often but progresses slower.
.
Gingivitis is the first stage of periodontitis. Therefore, if gingivitis is not stopped, the inflammation spreads to the bone. Indeed, one of the main causes of periodontitis is the significant presence of pathogenic bacteria that attack the periodontium, the tissue surrounding and supporting the teeth.
Other causes include a weakened immune system or smoking. If this condition is not diagnosed, the tooth may completely lose its support in the remaining bone and eventually fall out.
Periodontitis is a painless, silent disease that progresses month by month
Some signs may, however, be alarming to you – such as bleeding gums, certain teeth being loose, bad breath, or a bad taste in the mouth.
Periodontitis can cause the tooth to loosen – or indeed fall out.

How can it be treated and prevented?
Simply put, the absence of plaque prevents gingivitis – and without gingivitis, periodontitis cannot set in.
Excellent oral hygiene is therefore essential: daily brushing, morning and evening, with a soft bristle toothbrush and toothpaste that emulsifies plaque. For bacteria, the mouth is the main port of entry into the body.
For most patients, interdental brushes should complement this brushing, as they enable cleaning between the teeth, the main place where cavities and gum inflammation occur.
We also recommend the use of a tongue scraper once a week, especially for patients who smoke.

In addition to this daily and rigorous hygiene, we recommend dental scaling every 6 to 12 months to maintain perfect oral health.
SUMMARY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES
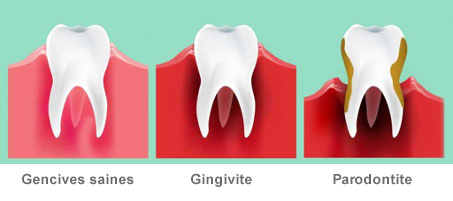
Find out more at www.parodontologie.ch.
If you would like to learn more about pedodontics, feel free to contact us to schedule a first consultation : Appointment