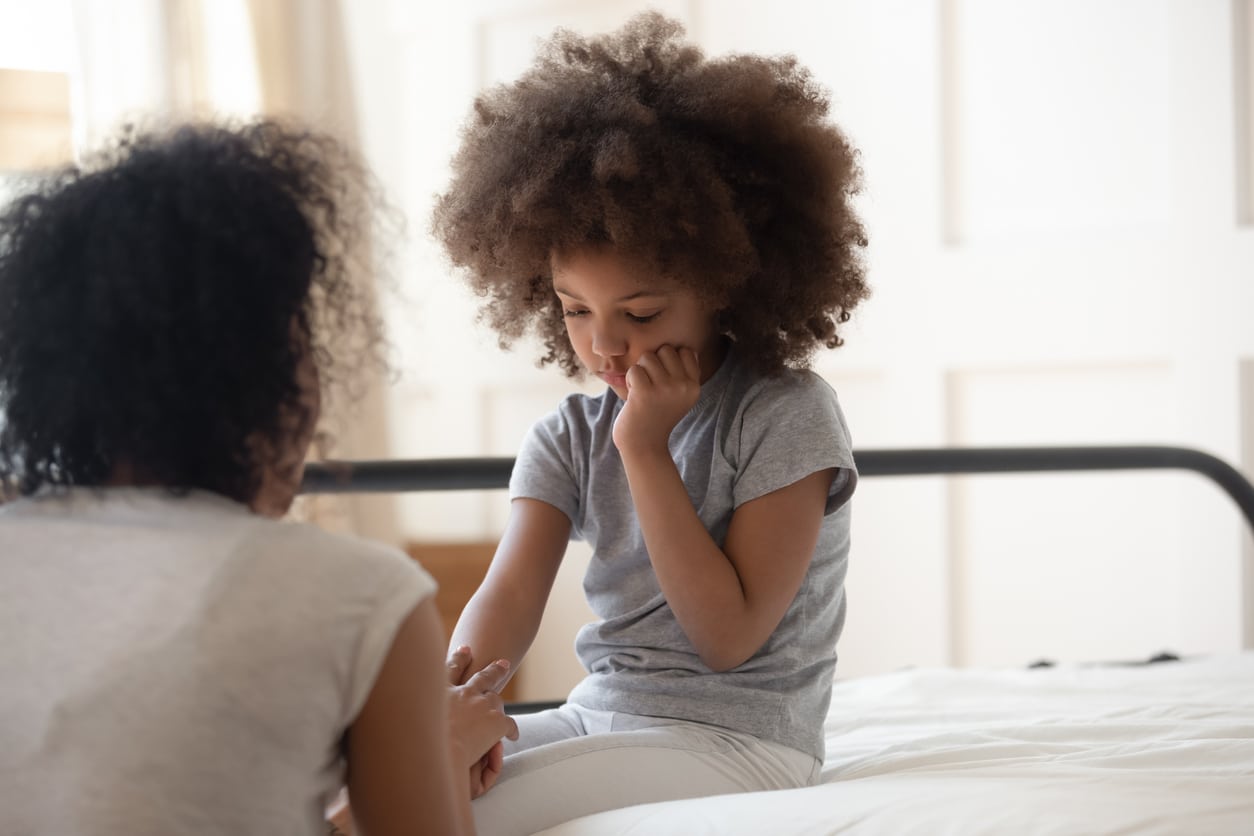
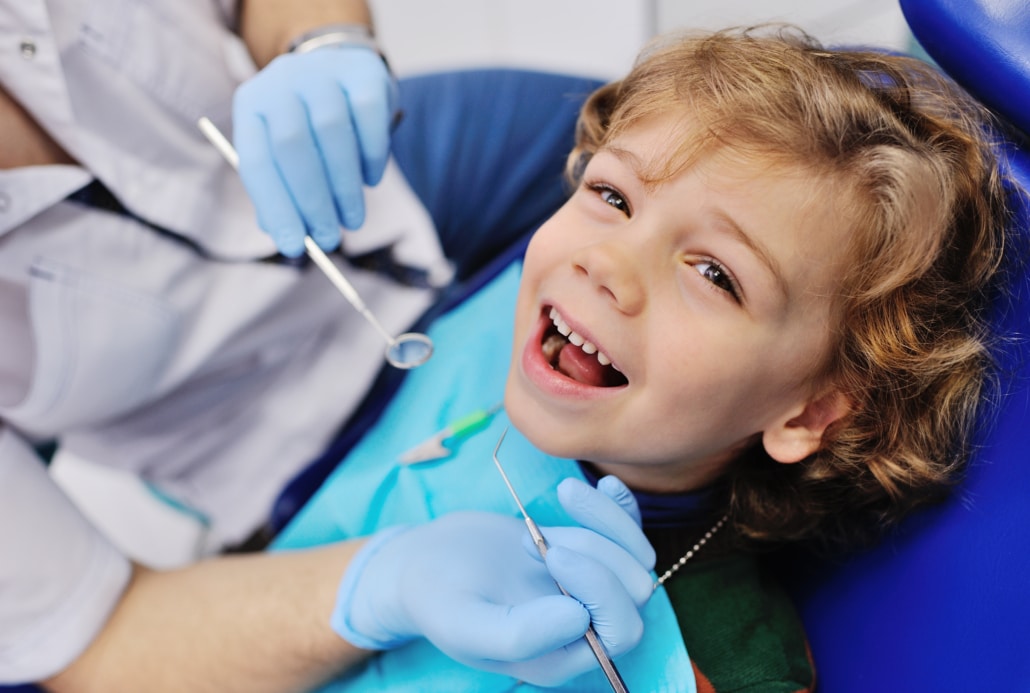
It is important for us to offer reassuring and caring dental care for children.
We encourage dental visits from an early age to eliminate fears and instil good oral health habits in your children.
A first consultation from the age of 4 allows your child to become familiar with the dental office environment outside of a painful context.
In addition, early dental examinations make it possible to identify and intercept future problems. Prevention is at the heart of our approach to children’s care.
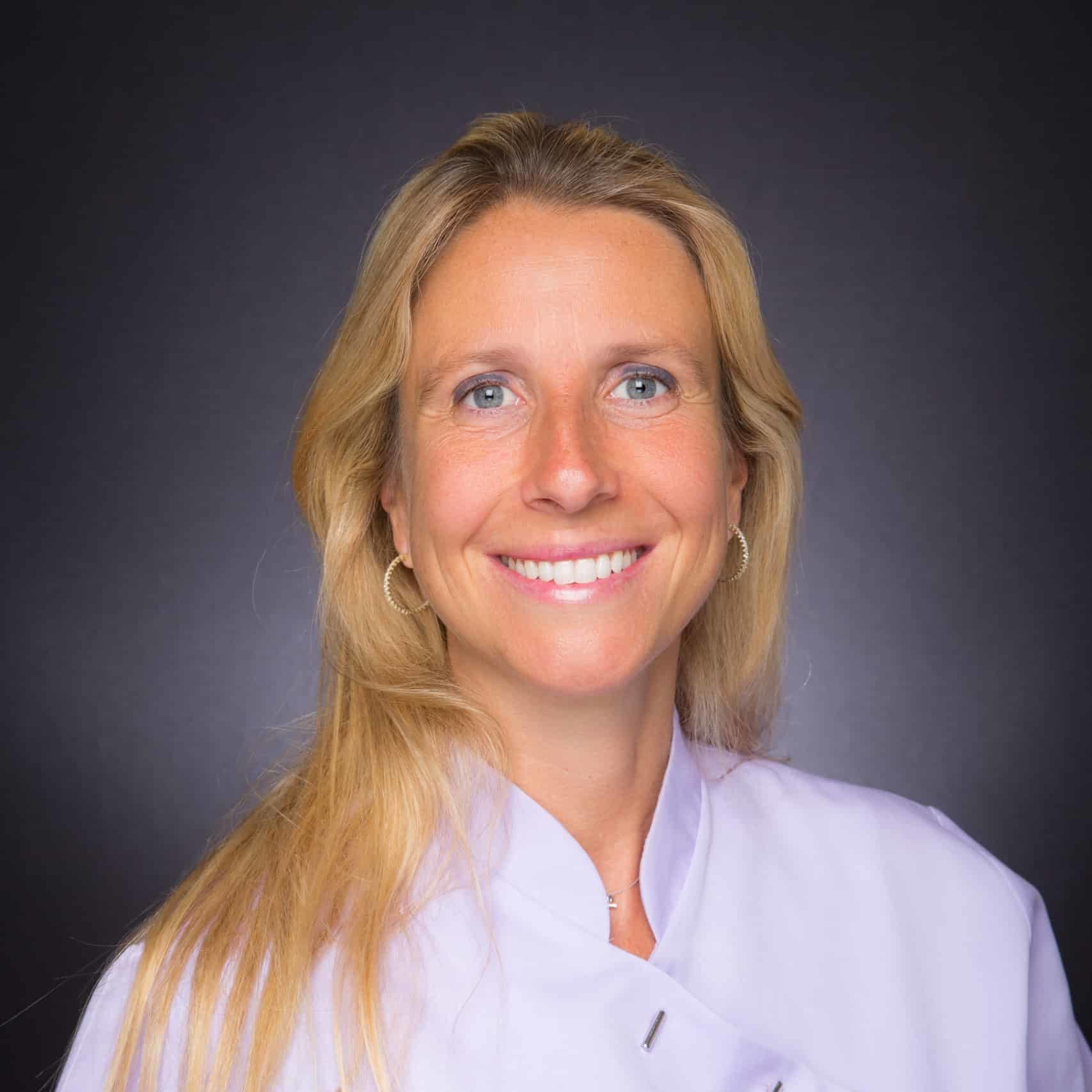

’I like to learn every day, to become better. Better for my patients, for myself, and for Smile and Care.’
Dr Mireille Frehner, dentist specialising in orthodontics
Discover the interview with Dr Mireille Frehner here.
Our dental treatments for children

Care and emergencies 6 days a week, Monday to Saturday
Did you know?

We welcome children of all ages, six days a week.
Our two dental clinics dentaires,based in Eaux-Vives and Grand-Saconnex, are staffed by paediatric dentists and orthodontists who are passionate about their profession.
Our dentists communicate with patients in almost every language!
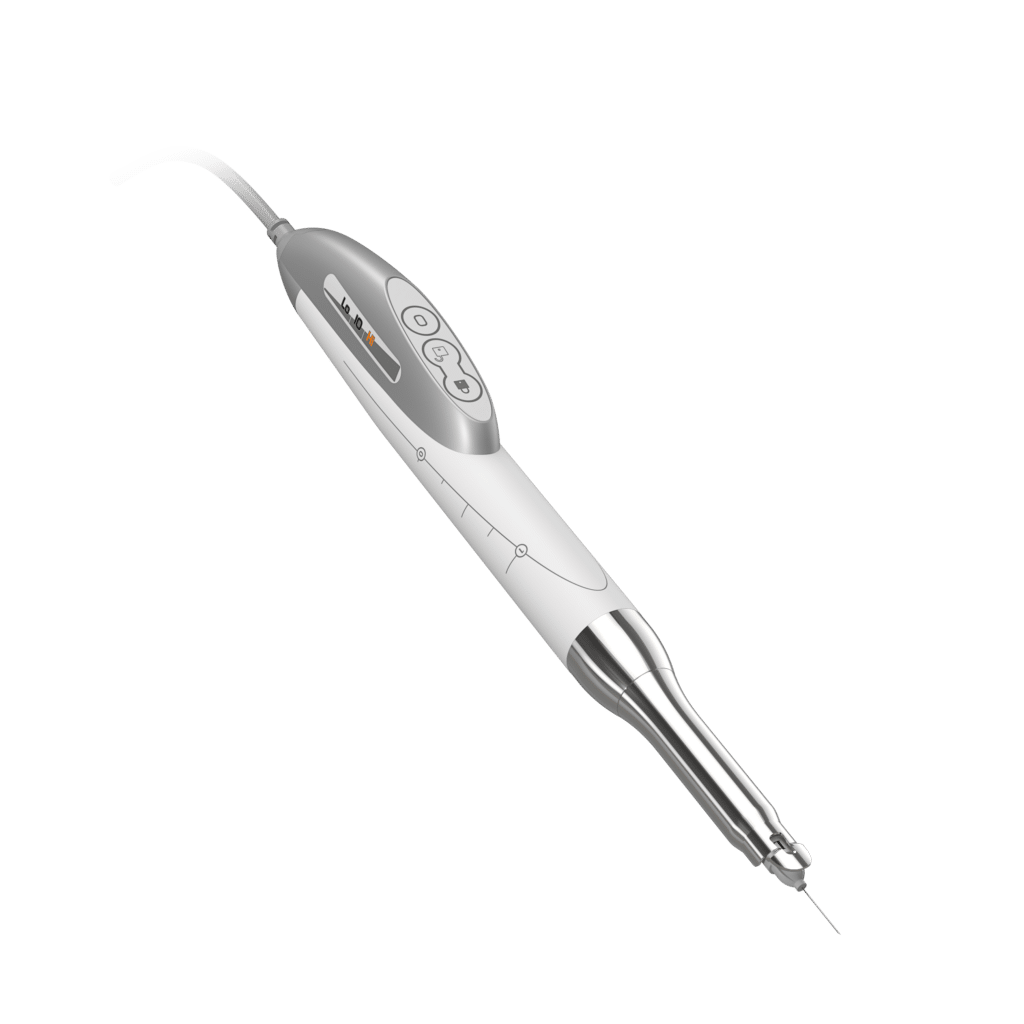
Quicksleeper, for painless anaesthesia
Thanks to this solution, no more fear of injections! The fear of pain affects a large proportion of our patients, both children and adults. To avoid painful anaesthesia, our dentists and paediatric dentists use an innovative and effective anaesthesia technique called Quicksleeper.

Emergency management
In the event of a dental emergency, it is important to make an appointment as soon as possible.
In the case of dental trauma (falls, broken, displaced or lost teeth, discoloured teeth), the paediatric dentist will provide emergency treatment, inform the parents and monitor the child. He or she will collaborate with other specialists if necessary.
.
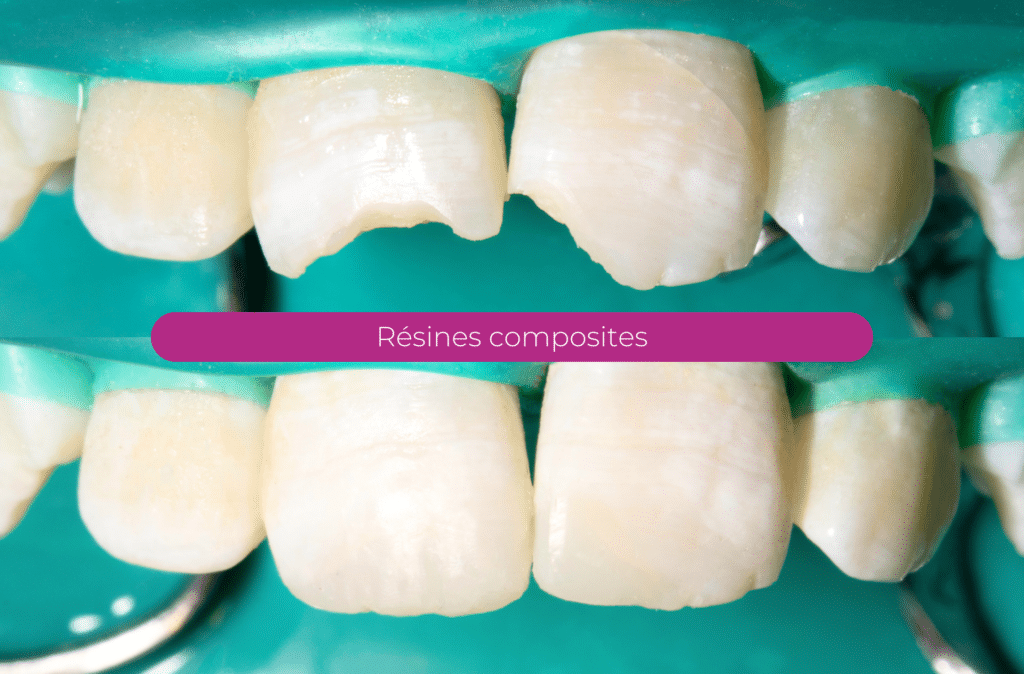
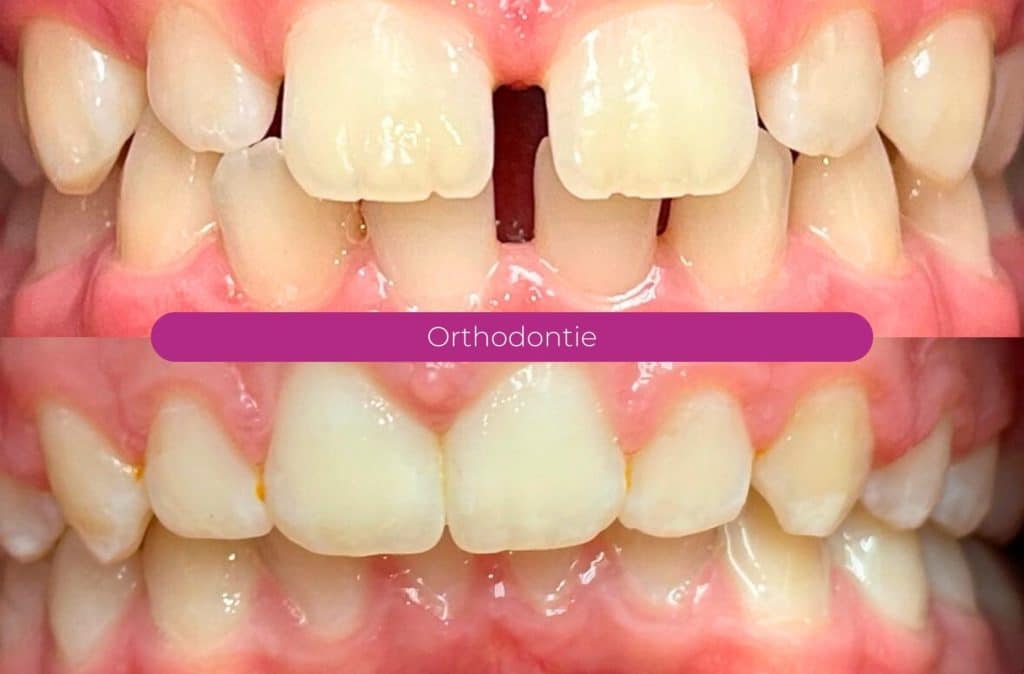
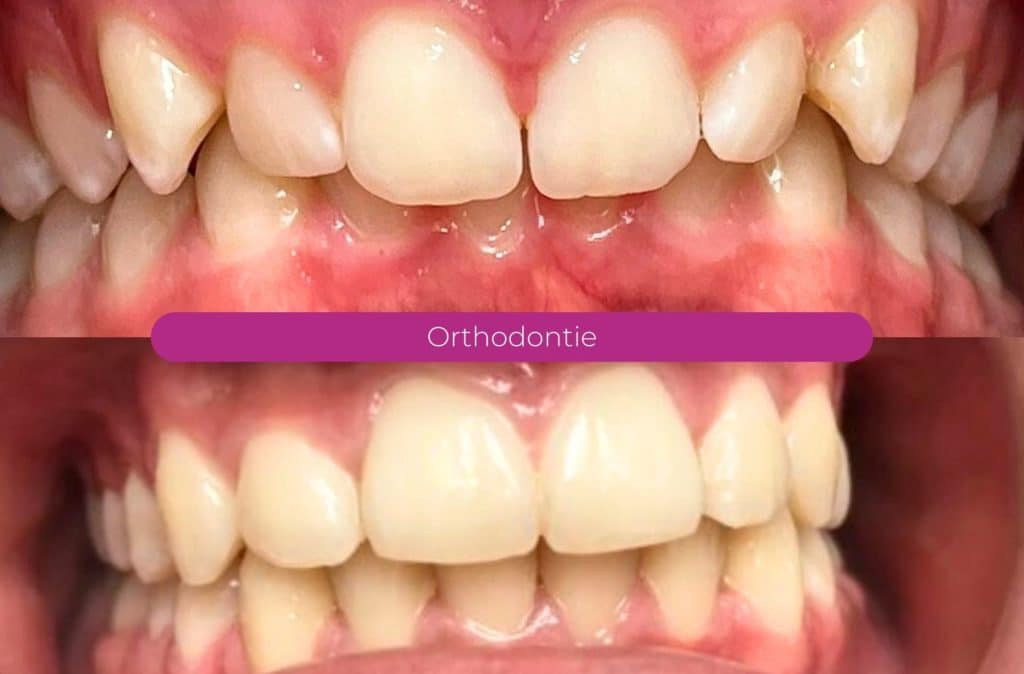
Your children's smiles, before and after
Make an appointment at one of our two clinics