Definition
It is important for us to offer dental treatments for children that are reassuring and caring. The most common surgical treatments, such as simple tooth extractions, are carried out by all the dentists at the Smile and Care dental centres in Grand-Saconnex and Eaux-Vives. The high-quality training they receive, as well as their acquired experience, enables them to take charge of the most common surgical treatments.
In our clinics, more complex surgical procedures require the experience of a specialist who practises exclusively dental surgery.

Extraction of impacted teeth, odontomas and supernumerary teeth: What you need to know
Tooth extraction is sometimes necessary to treat anomalies such as impacted teeth, odontomas or supernumerary teeth. These situations can cause dental complications and require surgery to preserve oral health and avoid functional or aesthetic problems.
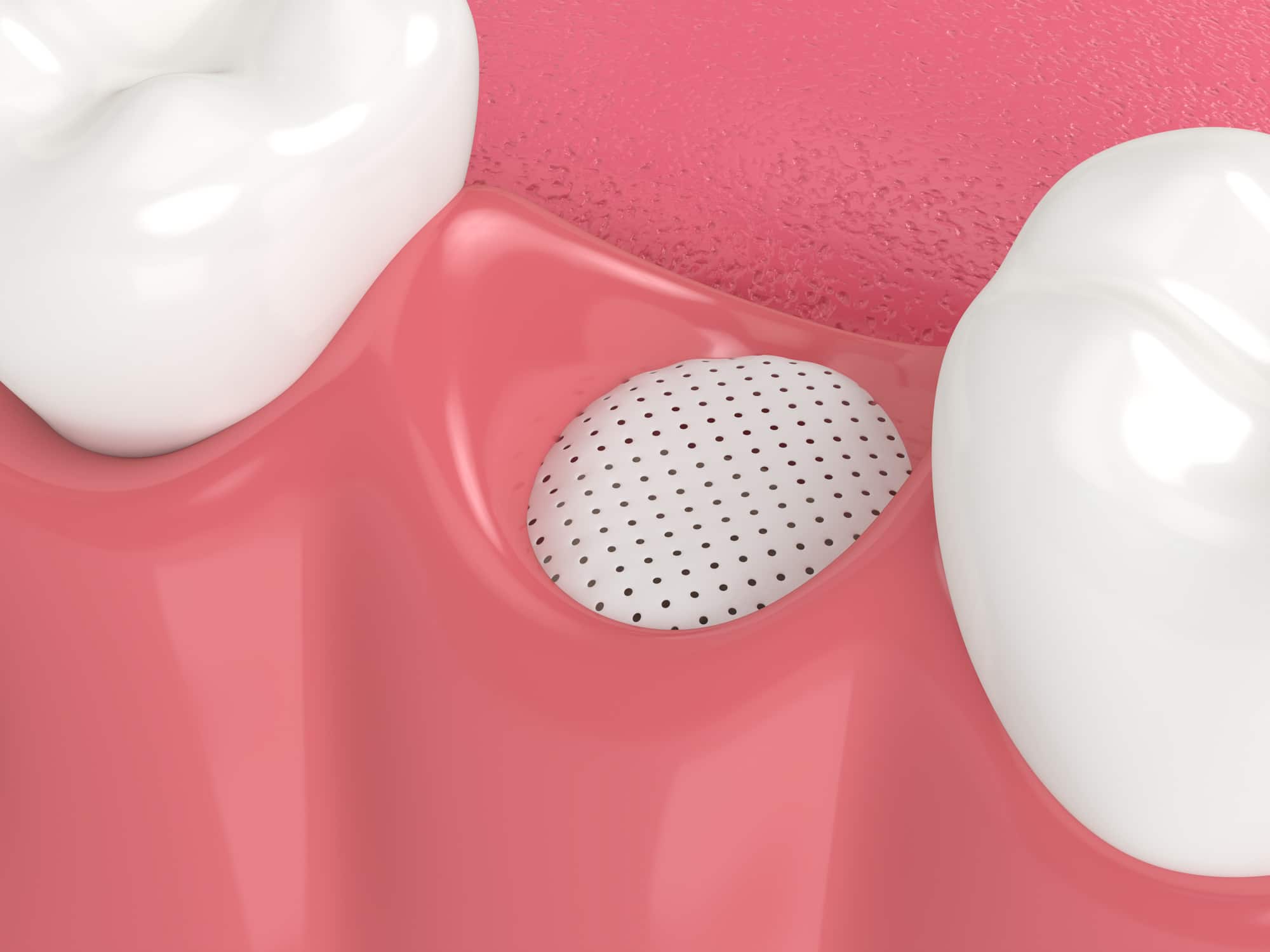

Bone grafts, with or without the simultaneous insertion of a dental implant
An implant is an artificial root inserted into the jawbone to replace a tooth. The implant is shaped like a screw.
The bone surrounding it must be sufficiently dense to fulfil its supporting function. However, when a tooth is missing, the bone resorbs and the implant cannot be inserted. In this case, a bone graft is common.
Frenectomy: Surgery on the labial frenulum, often at the request of an orthodontist
When a frenulum prevents normal tongue mobility, it can be removed under local anaesthetic.
Frenulum abnormalities can lead to orthodontic problems, such as misaligned teeth or a narrow palate. This is why the operation is most often requested by orthodontists.
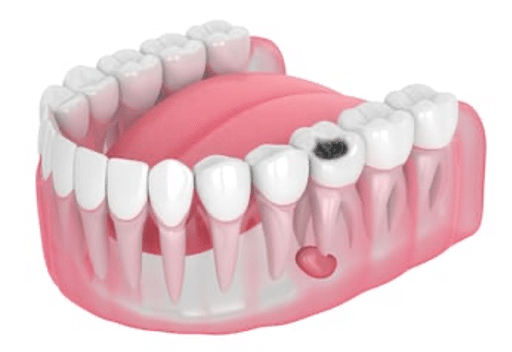
Cyst removal
A dental cyst is the formation of a small (round or oval) lump inside the jawbone at the tip of a tooth root. It can be caused either by infection or by an accident.
The most common symptoms are pain and unusual bad breath. This dental infection may be infectious, or the cause may be accidental. Even if these cysts are benign, they must still be removed.
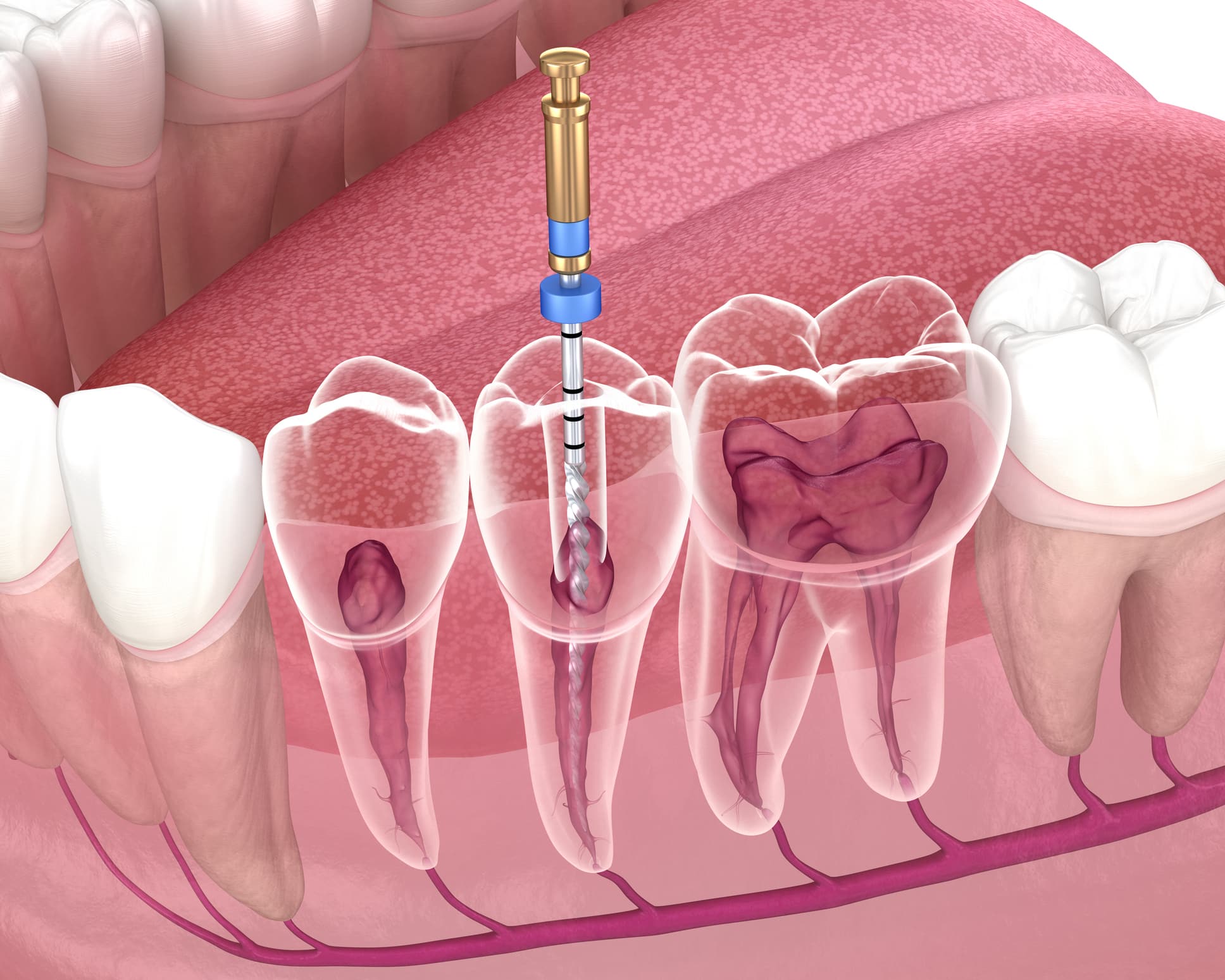
Endodontic surgery
Endodontics is the branch of dentistry that treats diseases of the inside of the tooth, particularly diseases of the pulp and dental nerves.
This type of surgery is indicated when endodontic retreatment by the ‘natural’ route is impossible, for example when a crown cannot be removed or when retreatment has not resolved the infection. The aim of endodontic surgery is to eliminate the infection by a surgical approach, then to disinfect the tooth by going through the root and not through the dental crown.
Our other treatments
Make an appointment at one of our two clinics